Test
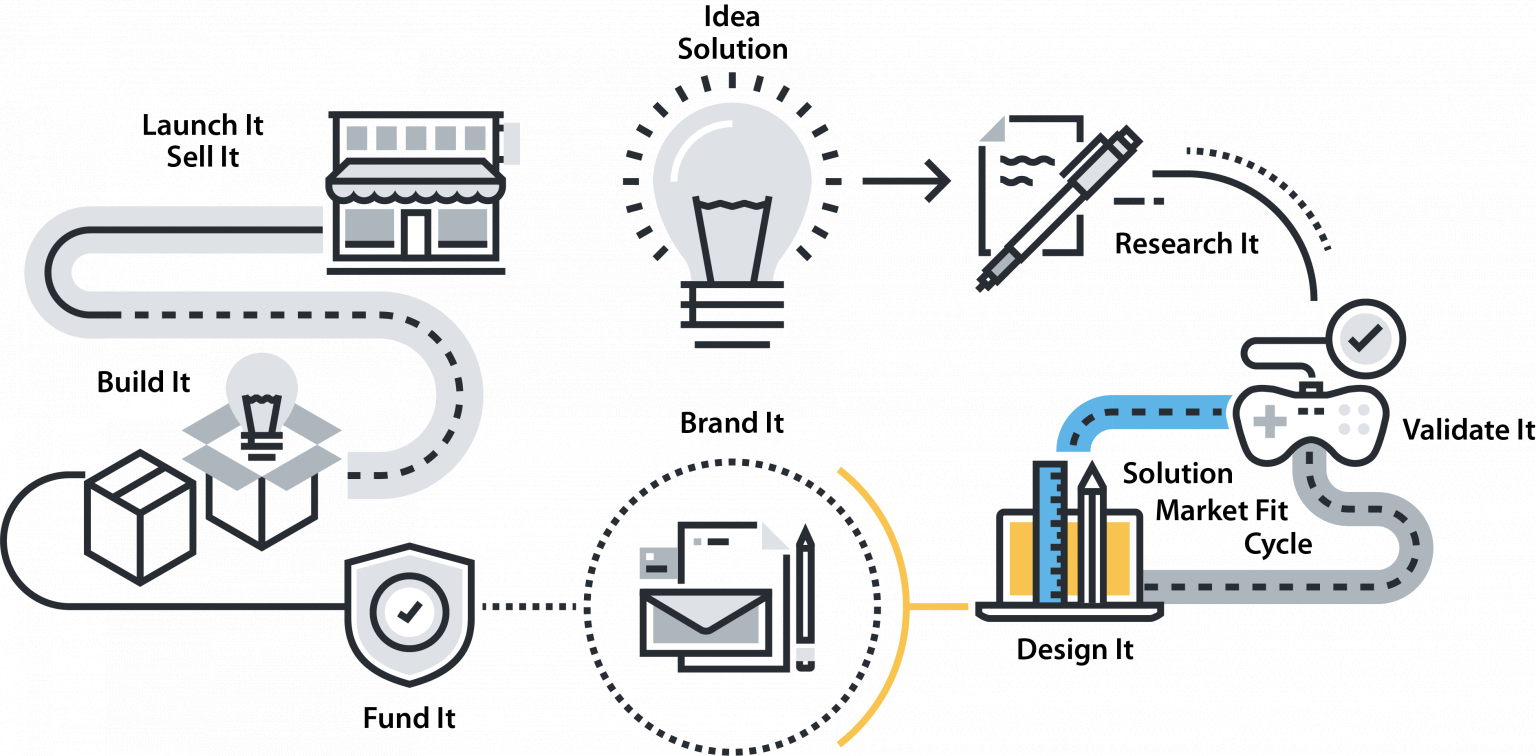
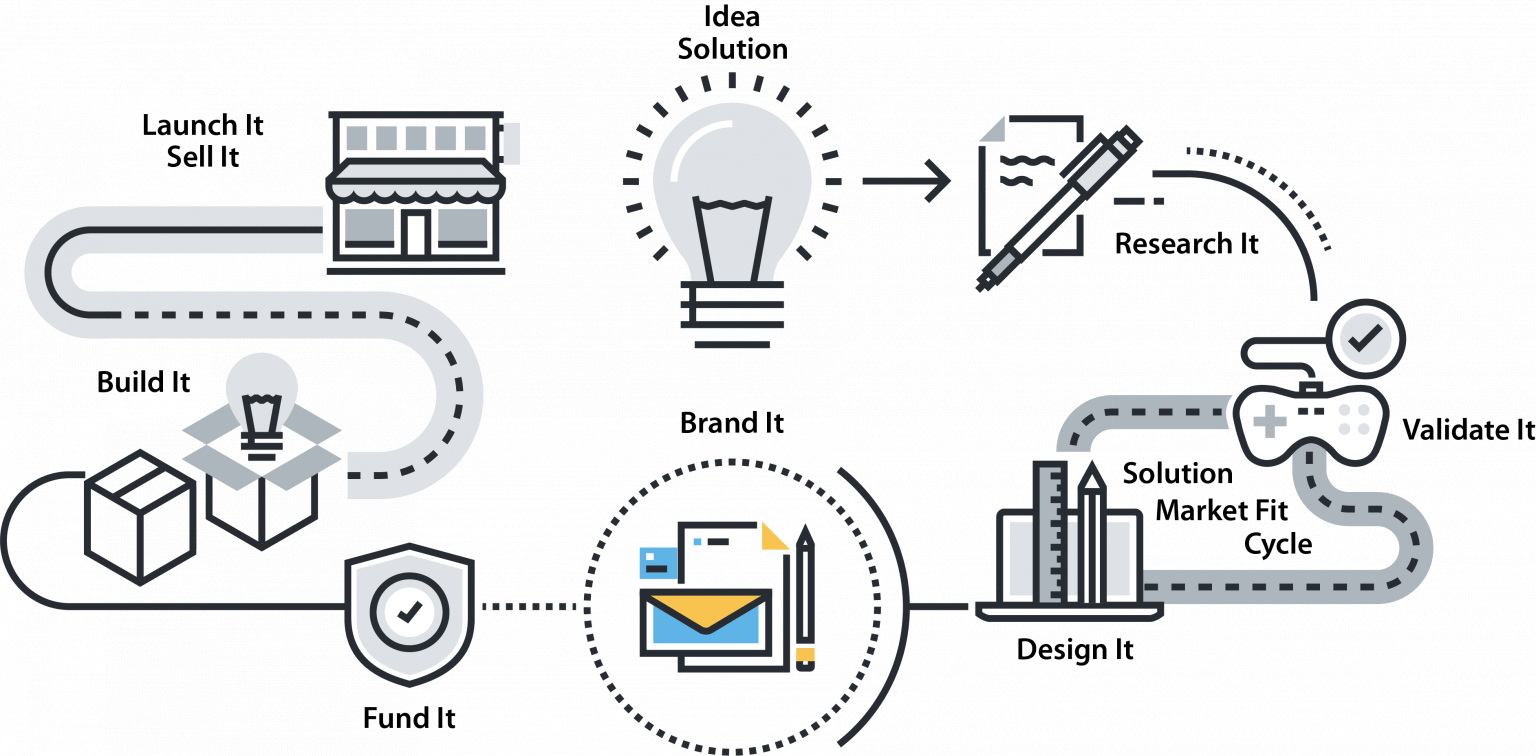
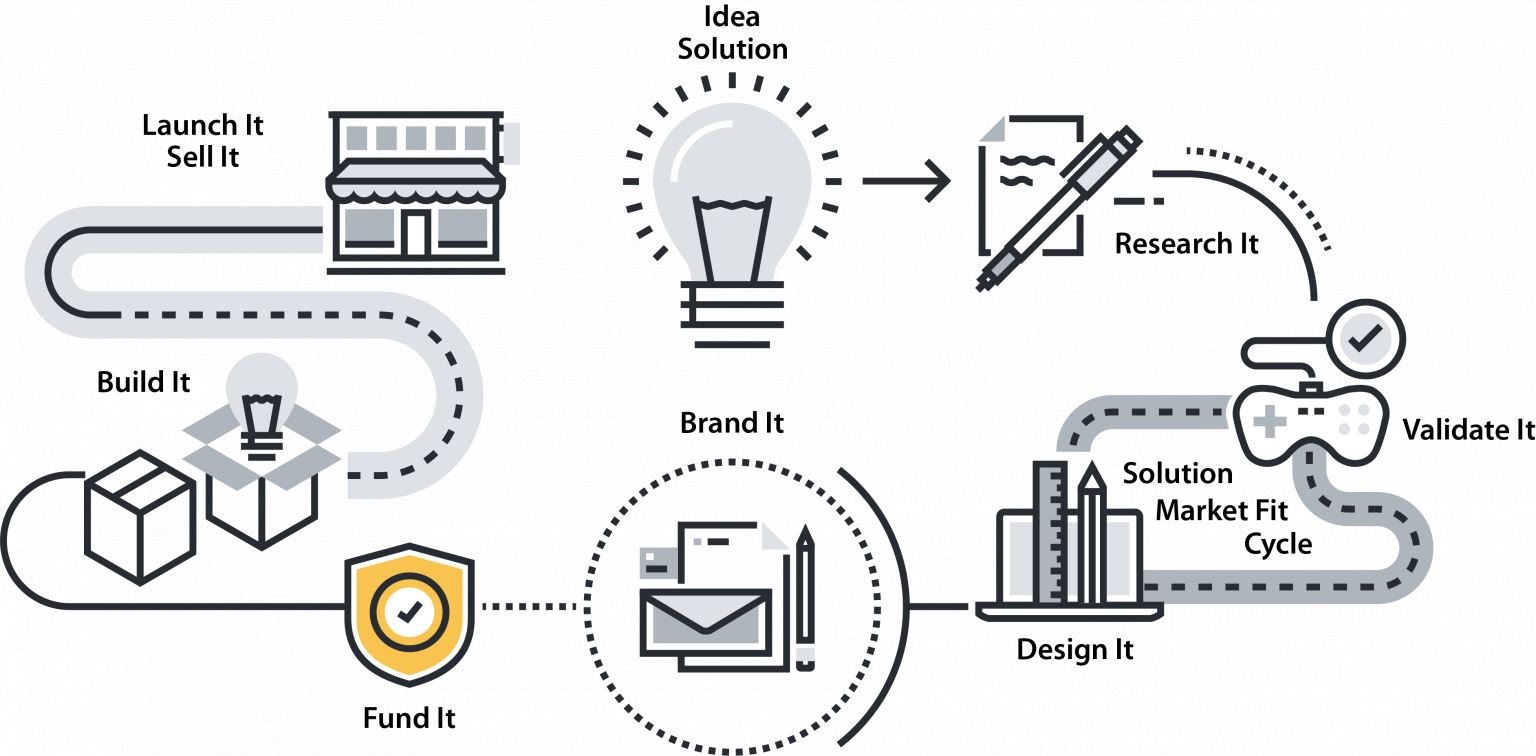
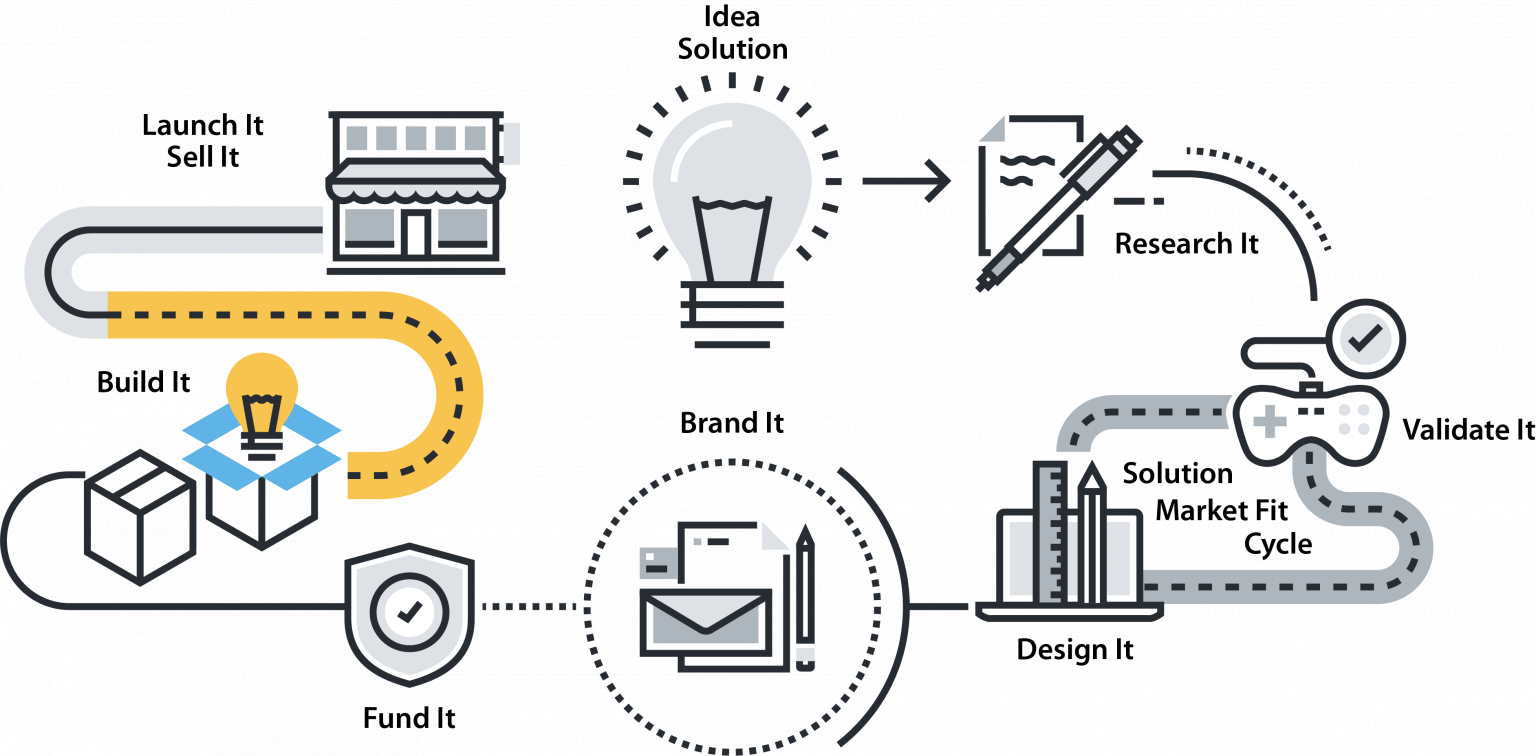
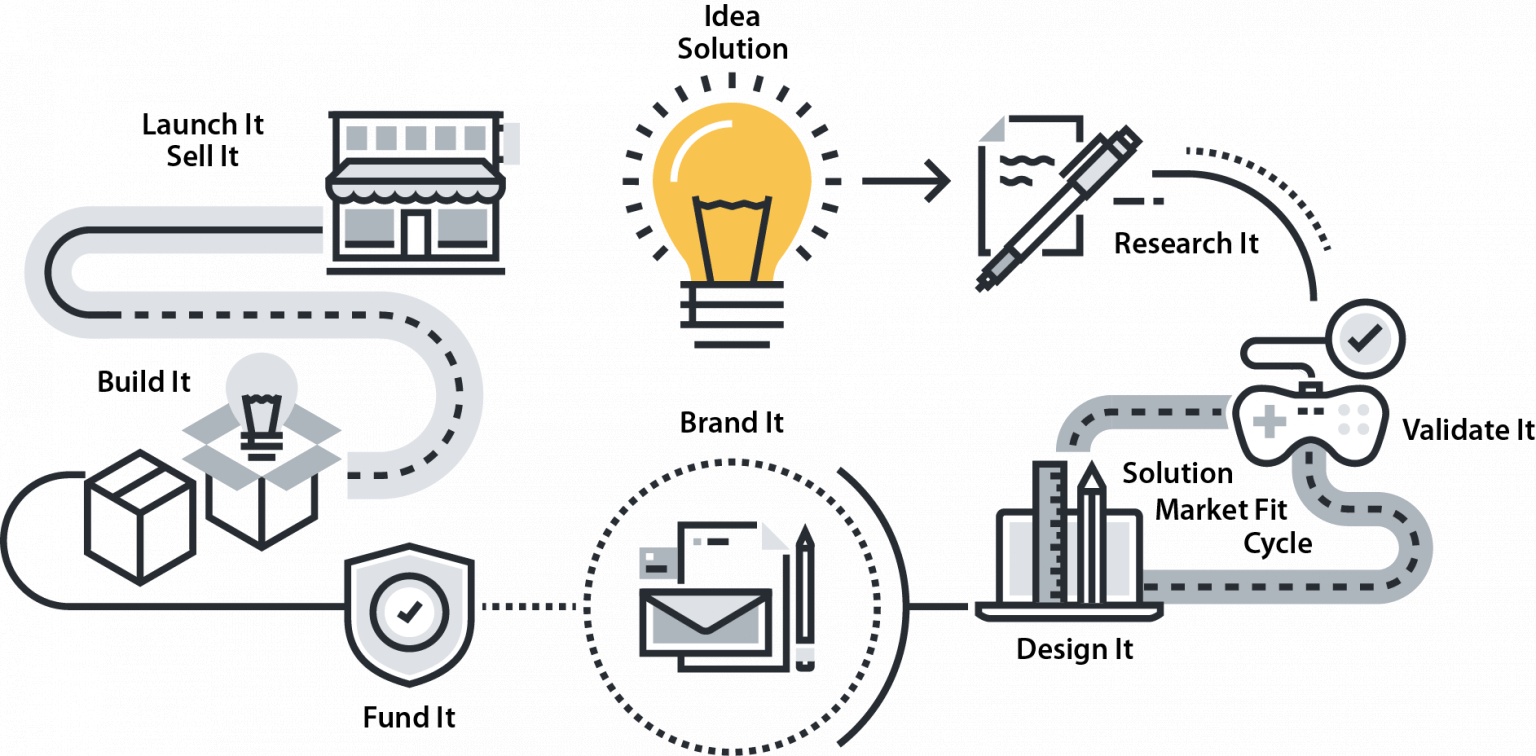
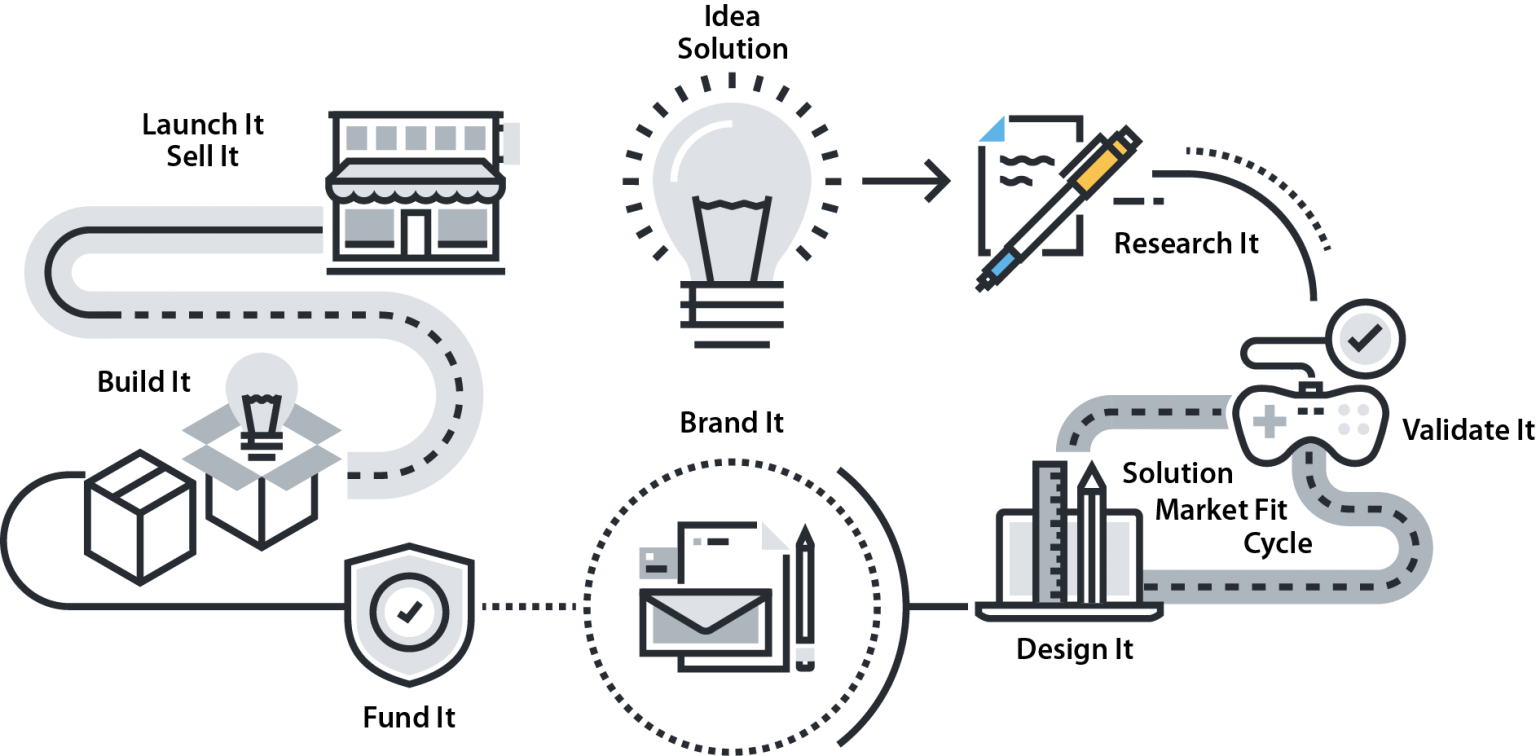
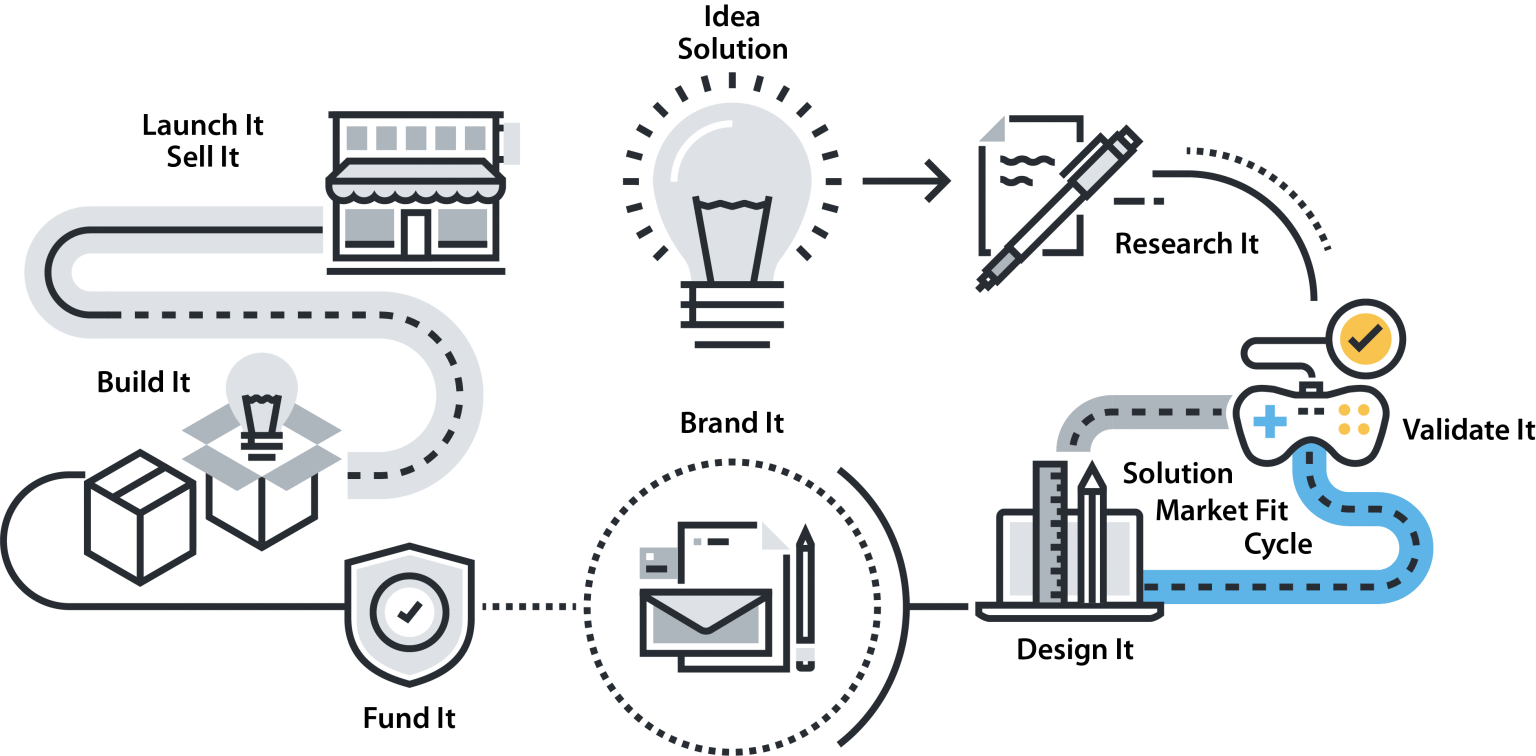
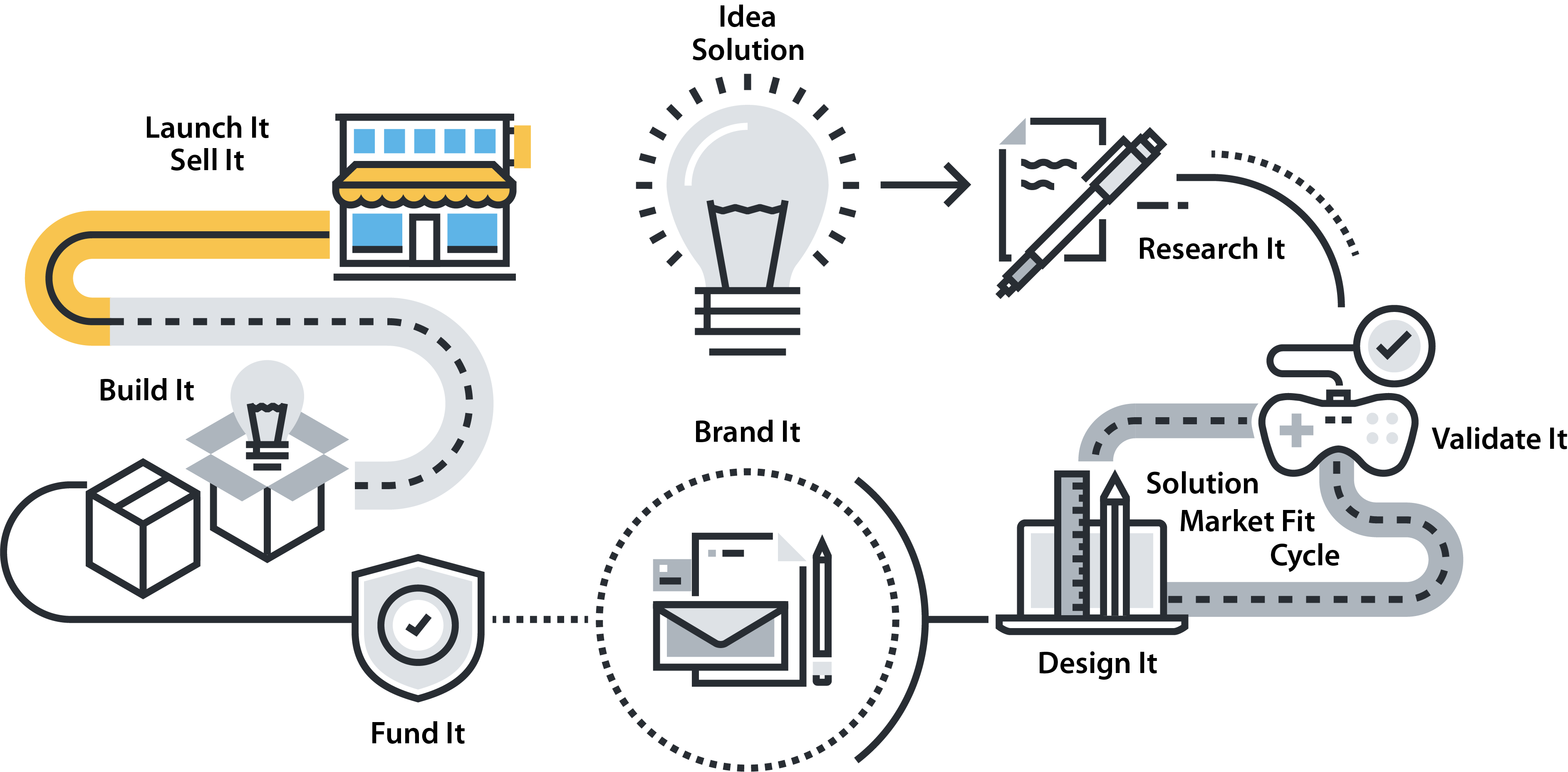
IDEA / SOLUTION
THE INITIAL SOLUTION
How do I start to organize my thoughts around my potential business?
Use a framework to get your initial thoughts out of your head and onto paper where you can start sharing it with others. A whiteboard or empty wall with post-it notes is a great alternative to an electronic document. Many frameworks exist, the key is finding the right framework for you. We have listed below the most common three. Check out our Toolkit for others, if you want to explore your options.
- Get your initial thoughts into a framework. You do not have to complete the framework, just get your initial thoughts into it.
- Get up to speed on what is happening in your local entrepreneurial community and trends in the start-up world relevant to your type of business - Main Street, Micro-enterprise "Side Hustle", Research Based "Innovation", or Second Stage "Existing business poised for a second growth stage".
- Grow Yourself. Start Learning your Strengths and Your Weaknesses
- Adopt a Growth Mindset. Your first idea/s may fail. Most successful entrepreneurs fail SEVERAL times before launching a successful business. But they will all tell you that it was part of the process. Don't give up. Your goal is to fail quickly and cheaply and use what you learn to launch your next idea.
Your Business/Your Product
- Business Model Canvas
- Lean Canvas
- Traditional Business Plan(s)
- Get Connected: Sparkyard (Local to DFW)
- Do not spend any money.
- Do not incorporate.
- Do not pay for a logo and slick marketing materials.
- Do not spend money until you know more about your potential solution.
- Do not give up if the first idea/product/business fails
RESEARCH IT
SOLUTION FEASIBILITY
Can my solution be profitable and what/who do I need to develop & implement my solution?
fea·si·bil·i·ty | noun | the state or degree of being easily or conveniently done.
Researching and validating your solution are the two most critical aspects of a startups potential success. You are expected to be an expert on your solution and be very informed on industry trends. Secondly, you need to define what skills are needed to provide your solution to your potential customers. Many entrepreneurs routinely skip over thoroughly researching their solution, the industry, and the competitors because they are eager to get started building their solution. However, it generally leads to the problem identified below. A solution no customers want.
CB Insights did a study of 101 start-ups asking the founders and investors why those companies failed. They categorized the results into 20 aspects. The #1 reason: 43% of those surveyed cited "No Market Need" for the solution those companies built. The #3 Reason: 23% of those surveyed indicated the companies did not have the right team in place to implement.
The key learning is do your homework and become the expert people will expect you to be. For some who are industry insiders this might take you a matter of weeks. Yet, for those that are creating solutions to enter a market or industry they are not familiar with it could take months.
- Complete a financial analysis that tests if the company can make money and how long it will take to become profitable.
- Determine what core skills your company will need in the early stages and if you have the right people involved to fill those skill needs.
- Document and map out everything you can about the industry, competitors, and the specific market using your chosen framework(s).
- Problem Statement Canvas
- SBDC - Analytics Platform (Coming Soon)
- Spread Sheets - Financial Analysis
- Google Advanced Search
- Do not skip this phase.
- Do not relay on untested assumptions.
- Do not hire someone to do this research.
- Do not create an investor pitch deck.
- Do not seek investment for your startup to build a prototype.
VALIDATE IT
RUN EXPERIMENTS
How can I test the market without building an actual functioning product or service?
vi·a·bil·i·ty | noun | ability to work successfully.
This is the most misunderstood phase of building a successful startup. You want to prove your assumptions and get early feedback on the strength and importance of your solution. Chances are as a early founder you have heard the term MVP "Minimum Viable Product". Many would argue, and we at Accelerate DFW agree, that "product" should be taken out of this term. Your MVP does not have to be a minimum product or the minimum services at all. You simply need something that helps you demonstrate your solution so you can receive feedback from potential customers about your solution. As stated before, the biggest reason startups fail is because they build something no one really wants.
Validate, Validate, Validate... There are two (2) aspects of your solution that you need to validate with your potential customers.
- The priority of the problem in the customers overall daily / weekly activity.
- The interest in the solution that you are wanting to offer.
- Gather enough feedback to confidently gauge the level of problem importance & the demand for the solution.
- Gather feedback and idea for potential pivots to your solution or other applications for your solution.
- Determine your ideal target customer profiles for early adoption of your solution.
- Minimum Viable Product Template: Cheat Sheet
- Pain Point Experiment
- Solution Experiment
- Customer Validation - What Do You Ask, with Justin Wilcox
- The Lean Startup: Build-Measure-Learn Feedback Loop
- Survey Tools
- Example: Zappos, Dropbox, Buffer
- Betalist Examples
- Do not build a "lite" version of your product or service.
- Do not build your app / website or prototype.
- Do not pay someone to build your app / website or prototype.
- Do not "sell" your solution.
This is where most entrepreneurs make their biggest mistakes. They start with the next section, Design It, before they have validated the idea, the problem and the solution. The #1 reason startups fail: 43% of those surveyed cited "No Market Need" for the solution those companies built. Avoid this mistake, validate with your potential customers before you build anything!
Stage-Gate: Go / No Go
DESIGN IT
PLAN YOUR COMPANY
What are the important aspects / features of my solution that potential customers care most about?
This is where you start to make some important decisions about your product and your company. Many of successful startups have built their initial product / service in a way that they knew they would have to start over for version 2. Why would they do this? Because it is what they could build quickly and cost effectively. The product driving forces for this phase are designing for speed to market and maximizing customer value with only the most essential aspects / features. Great entrepreneurs are able to really show their stuff here, as they are resourceful!
Building Your Team
In this phase you will decide if you are going to be a solopreneur, a micro-enterprise or if you need to build a founding team. Many main street businesses have a single founder and need employees. An office manager or store manager is a great opportunity to recruit someone with skills you don't have to strengthen the capabilities of your company. During the initial Idea Phase you took a few personality and skill tests. Now is the time to compliment your skills with others. If you know you need to have a founding team them you need to start looking for potential co-founders while you network and explore the world of startups. Founders rarely have all the skills needed to build both the product/service and the business. If you are a solopreneur, one founder/owner, then think about what skills you need to hire out. However, when it comes to your product / service you should be making it yourself as apposed to hiring an outside firm to build your product for you. Building a company means building a team. Highly effective teams create value way beyond just the product or service. Start recruiting to fill the skill gaps.
- Create your initial product roadmap.
- Bring on co-founders, key team members.
- Incorporate your business.
Product
- WordPress
- Raspberry Pi / Arduino Boards
- Maker Community
- Sketch-Up
- Y-Combinator - Startup School
- Customer Feedback Process
Team
- Defining the teams skill sets
- Co-founder Meetups / groups / platforms
- DISC Skill Set Analysis
- 16 Personalities Strength/Weakness Analysis
- StrengthsFinder Analysis
- Background Checks
- Do not "feature pack" your solution.
- Do not trust your instincts, verify peoples skills / backgrounds.
- Do not stop networking.
- Do not outsource your product or service.
BRAND IT/MARKET IT
SOLUTION PACKAGING
What impression do I want to give to my ideal customer base?
Customers tell you everything you need to know about how to sell to them, what to sell to them and how it should be priced, if you gave them ample opportunity to do so during the validation stages. If you are struggling here to determine what to say and why you are saying it then revisit your validation data or go get more validation from potential customers.
Marketing is the quintessential example of going down a rabbit hole. For instance, have you ever wondered why so many company logos are blue? All colors convey a non-verbal message, an emotional response. First off, it always ranks as the most universally liked color. Secondly, it conveys the emotions of creativity, safety / serenity, trust, dependability, and is associated with intelligence. It makes for a great logo color when customer loyalty is a key business factor. (How AccelerateDFW chose it's new brand color).
Short Term Critical Success Factors: When thinking about how much marketing effort to take on and how far down the rabbit hole you go think about what your short term business goals are. Create your marketing plan based on only these goals.
- Determine your company vision, mission statement, and values.
- Create your brand, the perception you want to convey in the eyes of the customer.
- Create your strategic marketing plan. (Business Goals, Marketing Goals, Target Customer Profiles, & Campaigns) (Be-aware: You will find a lot of confusion and contradiction about these subjects. Strategic Marketing vs Tactical Marketing. Campaign vs Advert. Marketing is messy.
- Lean Canvas - Unique Value Prop, Customer Segments, Channels
- Smart Goals
- Canva
- Logo Maker Tool
- Explainer Videos
- Don't adopt an "everything but the kitchen sink" approach.
- Do not start with tactics. For example: Facebook / Google Advertising.
- Do not try to market to everyone, thus targeting no one.
FUND IT / PROTECT IT
THE INITIAL SOLUTION
What kind of funding does my company need?
It does not matter if your are a main street business, a micro-enterprise or a tech startup, working capital is essential. However, you might be surprised to find out how most startups fund their endeavors, (Where startups get their funding). The most common misunderstanding in the startup world is when investors are interested in investing in a company. Spoiler: it is not in the early days of an idea with no prototype or validation that a sufficient market exists for a solution. Funding comes from many places, these are the most common: Founder savings, founder credit cards, friends & family, bank loan(s), grants, VC / angel investors, competitions and bootstrapping (organic via sales).
How do I protect my solution / company?
If you have true IP or a patent-able innovation then great. However, most companies do not have anything unique in these aspects. So the obvious question is how do they build their companies? Most companies these days take an off the shelf product / service and add a twist. A unique aspect that targets a specific audience that is currently not served or is undeserved. They then fortify this with, for example, a strong brand presence or by building a partner, supplier network that is hard to replicate. There are many other ways to defend your business.
- Create your pitch deck.
- Create your business plan, for bankable companies.
- Bring on co-founders, key team members.
- Incorporate your business.
- Gain traction with customers / potential customers.
- Crafting an Investor Pitch
- Term Sheets
- What to know about VC funding
- Bootstrap
- Do not ask VC's to fund an idea.
- Do not be scared to tell people what you are working on for fear they will steal it.
- Do not rely on one type of funding pathway.
- Do not forget to "shop" patent attorney prices.
BUILD IT
BUILD YOUR SOLUTION
What do I need to build my product or service as quickly as possible?
In this phase you start building your physical product, service, main street business, SAAS platform, or what ever form your solution takes. In this phase time and perfection are not your friends. Many entrepreneurs get stuck here, constantly tinkering and never making it to the next phase, launch. You might need to make new relationships with potential suppliers or people who will deliver your service. You might have to learn some new skills or make some compromises on your dream product or service. This is your doing phase, talkers get left in the dust.
Keep in mind that the best companies approach this process as designing a feedback loop. Release, get feedback from customers, alter and release again, get feedback from customers, etc... The goal is to find the strongest product market fit as fast as possible.
- Get version alpha in the hands of your potential customers.
- Create an iterative product / service improvement process.
- Do not seek perfection.
- Do not be scared to tell people your solution.
- Do not hibernate while building, keep networking.
LAUNCH IT / SELL IT
SET YOUR SOLUTION FREE
What is the ideal way to introduce my solution to my potential customers?
This is where the rubber meets the road, getting a customer to pay for your solution. For those that have diligently done their research and validated their assumptions with potential customers, selling will be much easier. For those that simply built their solution and launched, this process might be painful. This is where you put your marketing plan to work. Align how you have segmented the market with a target customer profile and talk about your features / benefits and points of differentiation, simple as that. The hard part is getting to a point where you can talk to customers. For business to business sales it is usually compiling and working a list with sales calls, e-mails and networking. For business to consumers it is usually building product awareness, providing demos of the product and having a rewards program for referrals.
- Get version alpha in the hands of your potential customers.
- Create an iterative product / service improvement process.
- Product Launch Plan
- Marketing & Sales Funnel
- Crafting a Sales Pitch
- Marketing & Sales CRM's
- Do not give up.
- Do not forget to get continuous feedback from your customers.
- Do not think VC/Angel funding for mass marketing is the ticket.